What is liquid staking, and how does it work?
Liquid staking and regular crypto staking: how are the two different?
Why are people opting for liquid staking?
Top protocols in liquid crypto staking
Pros and cons of liquid staking cryptocurrency
What is re-staking?
Lido Finance and its monopoly in the liquid staking market
If you are willing to learn, the crypto space can give you a thousand and one ways to earn. Bad poetry aside, it actually is true: in the beginning, people thought you could earn only by mining and trading Bitcoin. However, in just over a decade of existence, the crypto world has invented numerous ways users can earn, aside from putting the $60,000+ you might just have lying around into one Bitcoin. Liquid staking is one of those avenues.
Ever since Ethereum started its transition into a proof of stake consensus, staking has been a term every crypto nerd and their mother have become familiar with. The Beacon Chain was key to this evolution, implementing the proof of stake mechanism. Further, the Shanghai Upgrade in 2023 unlocked all the ETH staked since the PoS shift began, taking Ethereum’s utility to investors to new heights.
In this post, we find out what liquid staking cryptocurrency in particular is, and why the Lido Finance protocol has gotten famous (or infamous) lately.
Any proof of stake-based (PoS) blockchain (and some other consensus mechanisms too) can allow staking cryptocurrency, which basically involves you acquiring some of the blockchain’s native crypto and locking it back on the chain for a set amount of time.
During this time, you earn interest on your deposits, and after that time is over, you can take back what you staked. People who stake on the blockchain directly are called validators, and they can even participate in adding blocks to the chain.
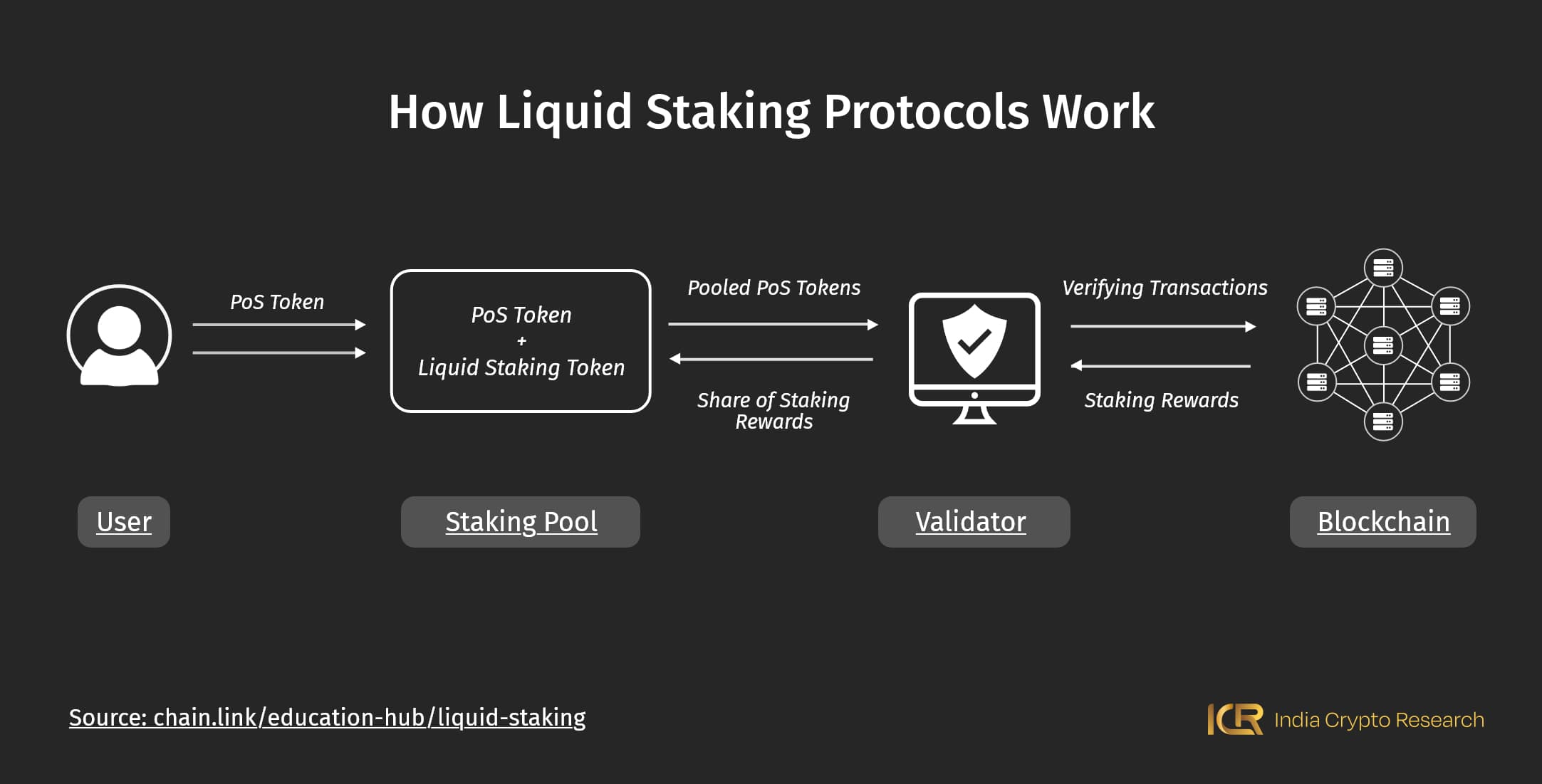
Now, liquid staking has a slight difference. In liquid staking cryptocurrency, you deposit the same coins with a liquid staking service provider instead of directly on the blockchain. A validator pools your contribution along with others’ and uses these funds to directly stake on the relevant PoS chain. You also get a ‘receipt’ to symbolise your deposit - these are LSTs.
LST meaning? They are liquid staking tokens. After staking your asset with a staking service provider, you receive an equivalent amount in liquid staking tokens, which you can trade and sell across DeFi platforms. You see how aptly they are named? They provide liquidity to you even when your actual native cryptos are staked.
We have already explored this a little, but here’s a broader explanation:
| Attributes | Regular crypto staking | Liquid staking cryptocurrency |
| Platform | On the native PoS blockchain platform | On a staking service provider, which pools deposits from users together to fund a validator node |
| Utility | You have to keep your assets locked up for a certain amount of time with only interest payments as staking rewards | In liquid staking cryptocurrency, you can earn LSTs or liquid staking tokens to derive use out of your crypto even when they are locked up |
| Rewards | You get interest on your deposit as staking rewards, and might also receive some more of the native crypto | On top of your share in these regular staking rewards (equivalent to your deposit), you also get LSTs which you later redeem when your deposited crypto is released by the PoS consensus mechanism |
| Minimum staking amount | PoS blockchains may have a certain minimum amount they ask to be staked; for instance, the minimum crypto staking amount on Ethereum is 32 ETH | Liquid staking cryptocurrency does not have a minimum amount you must own and deposit, they pool assets together from multiple stakers to fulfil the minimum quota for a validator |
Overall, liquid staking cryptocurrency definitely gives you an edge over direct stakers.
What’s not to like? You can earn rewards without giving up on liquidity for your assets during the staking period (while the rewards are around 4-6% for regular staging, liquid staking cryptocurrency can potentially fetch you about 10-16% of rewards), which is incentive enough to opt for liquid staking. After all, who doesn’t want to hit two birds with one stone?
Further, as mentioned before, Ethereum has a steep minimum amount required to stake of 32 ETH, for both native staking and competing to become a validator. This is clearly too expensive for most people, and centralised staking services like Coinbase and Binance take out a huge commission.
Your solution is liquid staking service providers, who allow you to stake a far smaller amount (even as little as 0.01 ETH), take care of the technicalities and stake on your behalf, and extract lesser charges.
Of course, make decisions only after evaluating the crypto tax landscape for your respective jurisdiction, and also the risk involved in crypto investments.
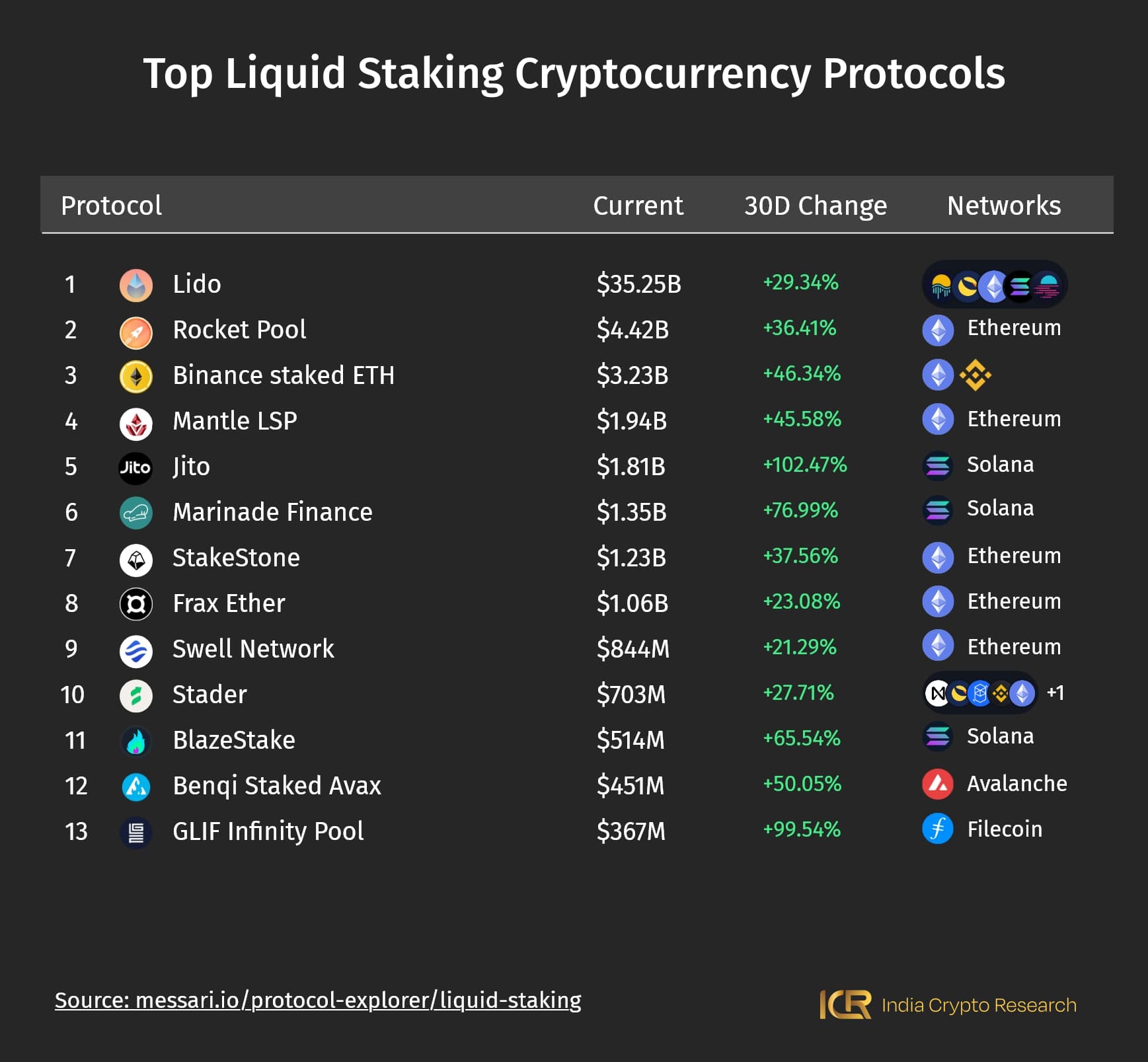
As Messari ranks them for the past year as of the beginning of March 2024, you can see the top liquid staking protocols in the image above. Lido Finance harbors the lion’s share, leagues and leagues ahead of Rocket Pool in the second position.
Since we were just talking about Ethereum staking, here’s how all 31,646,008 of the ETH staked at the time of writing divide up between different service providers and independent stakers:
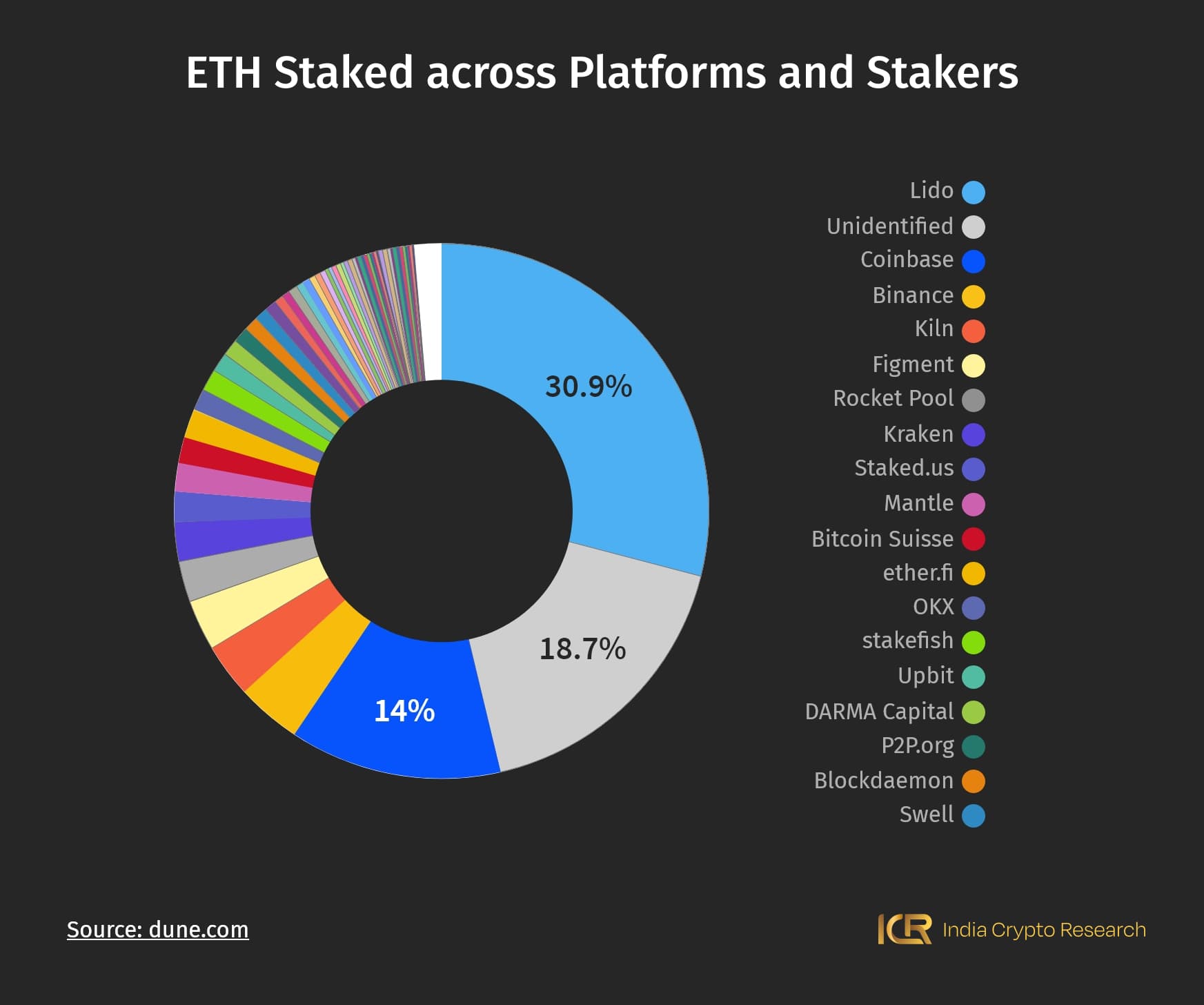
Again, Lido Finance has 30.9% of the total staked ETH; the number is a cause of concern for naysayers fearing centralisation for PoS Ethereum. If Lido faces any disruption, it may cause the entire Ethereum blockchain to get disrupted as well; it presents the threat of a single point of failure, after all.
How founded is the fear? We explore that later in this article.
What is an article without a pros and cons list to make your decisions for you? We’re here to serve.
| Pros of liquid staking cryptocurrency | Cons of liquid staking cryptocurrency |
| Increased utility for your crypto tokens is achieved with liquid crypto staking, because you can use LSTs while earning staking rewards on your original cryptocurrency. | A validator can be removed from a PoS network for bad behavior with the ‘slashing’ mechanism. If this happens, your staking rewards may be at risk. |
| You don’t have to wait for the lock-in period to end, you have the flexibility to engage in the crypto market in the meantime. | Platforms like Lido Finance can pose centralisation threats. |
| You have the freedom to pull diversification strategies (i.e. using the LSTs to acquire another token entirely) | There may be legal repercussions as crypto regulation is still opaque in India. In-depth research is required before you choose to participate in crypto staking, or crypto transactions of any kind in general. |
| You don’t need to own a certain minimum amount in a crypto to be able to participate in liquid staking cryptocurrency. |
Liquid staking cryptocurrency allows you the benefit of ‘liquid re-staking tokens’ too. Basically, you can use your staked coins as cryptoeconomic security on other platforms. In return, you acquire a part of the protocol fee and more as rewards.
For example, Eigenlayer is a platform that allows staked ETH- either natively or through liquid staking platforms- to be re-staked.
As we saw before, if we talk about liquid staking cryptocurrency, Lido Finance hosts the majority of the market. The platform is a liquid staking solution made for proof of stake cryptocurrencies, including Ethereum, Polkadot, Polygon, Solana and Kusama.
The platform’s TVL nears about $39 billion. For networks like Ethereum, its user base may pose a threat of centralisation in theory. However, Lido is an on-chain protocol with a DAO; the node operators here are therefore managed by the Lido DAO, which is in turn managed by LIDO token holders.
Lido is therefore a decentralised organisation at its core. Further, the DAO brings a set of public guidelines for any addition to its ‘alliance’ of node operators to ensure diversity and geographical distribution, among other things. All of these measures help avoid centralisation and in turn any issues arising from having a single point of failure for a decentralised blockchain.
There’s also the fact that any validator caught misbehaving will be slashed by the Ethereum PoS network, and similar methods are in place on other PoS blockchains too. This inherent mechanism prevents centralisation of power.
It stands to reason to still fear a single point of failure emerging from a platform like Lido and prepare accordingly. There’s a business opportunity here for other liquid staking protocols as well- to take over a share of Lido’s current user base and mitigate any threats of centralisation.
As the PoS platforms’ inherent blockchain technology works against efforts of centralisation, we can say any attempts to erect one central point of control for a chain is virtually impossible.
Well, that was it from our end on liquid staking cryptocurrency. Want to know more about the world of crypto and blockchain? India Crypto Research is your one-stop education hub!
India Crypto Research operates independently. The information presented herein is intended solely for educational and informational purposes and should not be construed as financial advice. Before making any financial decisions, it's essential to undertake your own thorough research and analysis. If you're uncertain about any financial matters, we strongly recommend seeking guidance from an impartial financial advisor.