Etherscan
Address
Transaction Hash
Token
Block
Domains
Summary

The world of crypto and blockchain is filled with buzzwords making it extremely difficult for newbies to visualize how a blockchain functions. Understanding the blockchain explorer is one of the most effective ways to speed up your web3 learning journey. So what exactly is a Blockchain Explorer?
A Blockchain explorer is a tool to view the information on a blockchain that includes transactions, fees, blocks, smart contracts, token information and much more. This is similar to a product metric dashboard to visualize everything related to the product.
A Blockchain explorer is not necessarily built by the creators of the Blockchain. Since Blockchain is nothing but a public ledger, anyone can create a Blockchain Explorer since anyone who runs a node on the blockchain has access to the blockchain ledger data.
Below are some explorers of popular chains:
Let’s take a look at etherscan the most popular blockchain explorer for Ethereum
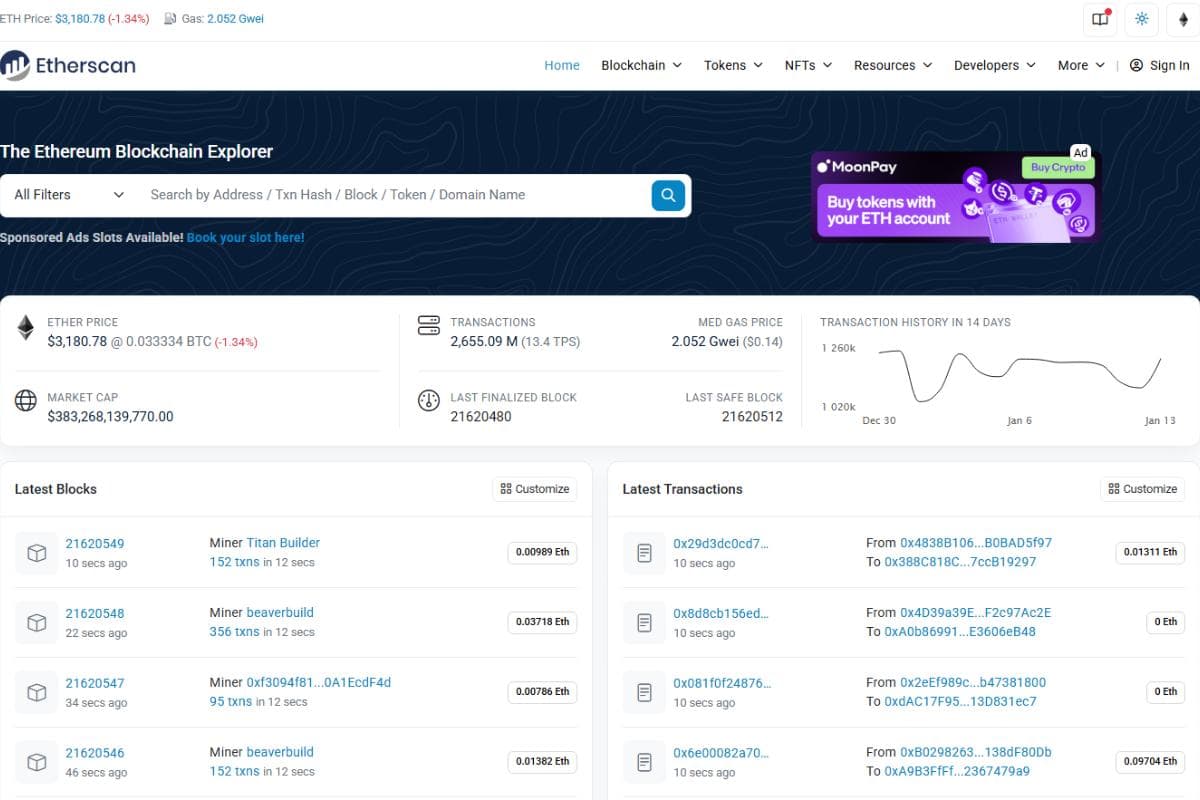
On the top, you can see information on the price of Ethereum and Gas Fee in Gwei (native units of gas in Ethereum). Gas Fee is the transaction fee on the Ethereum Network that would be distributed to the validators.
The Gas price of Ethereum is dynamic and sometimes spikes above 1000 Gwei depending on supply-demand dynamics. A gas fee below 30 Gwei is desirable.
💡Tip: You must always check the transaction fee before making a transaction since sometimes it can be unreasonably high, causing you to spend hundreds or thousands of dollars simply on transaction fees.
The Search bar allows you to search for any address, transaction hash, block, token, or domain name. Too many buzzwords again? Let’s simplify these first before moving ahead.
An Address is like an account number in a bank. It is the destination to receive and store your funds. When you want to transact on the blockchain, you create an account. The account has an address called the public key and a private key such that only you can access your account (i.e., create send transactions or deploy contracts).
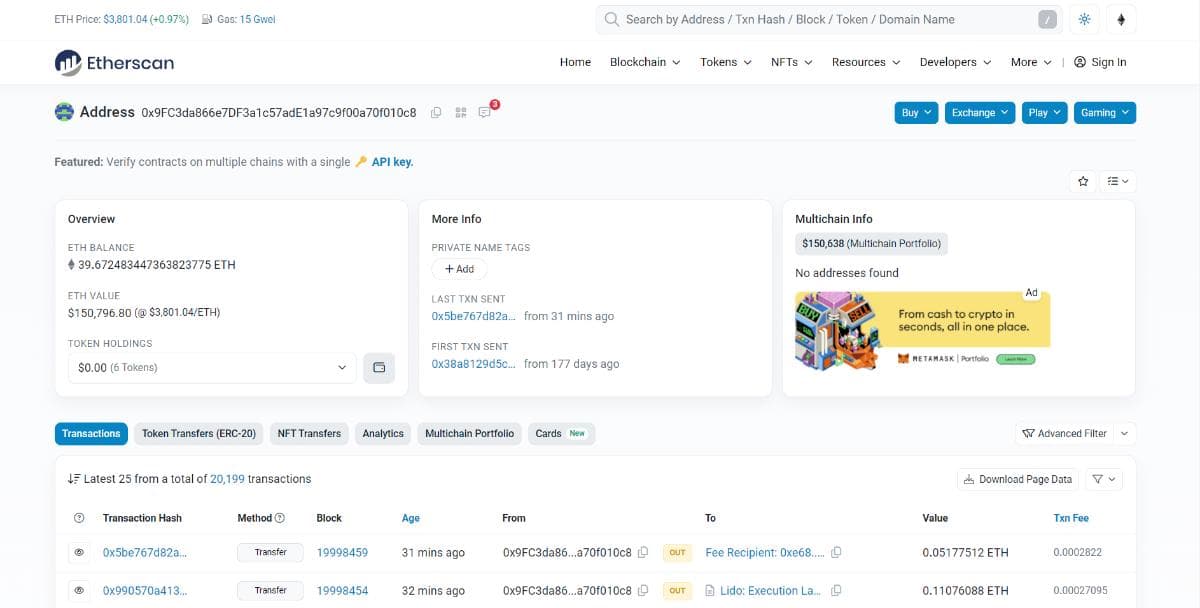
Searching by address opens the page of the address searched. You will be able to view the ETH balance, the first and latest transactions, and all transactions made by the account owner. Blockchain is a public ledger that maintains anonymity of the owner while ensuring transparency.
A transaction hash is similar to a transaction ID for a transaction you make in a bank. It is a unique cryptographic string used to uniquely identify any transaction.
💭Did you know? A transaction receives a hash as soon as it is made. However, it may not get confirmed if, for example, the gas fee setting is too low.
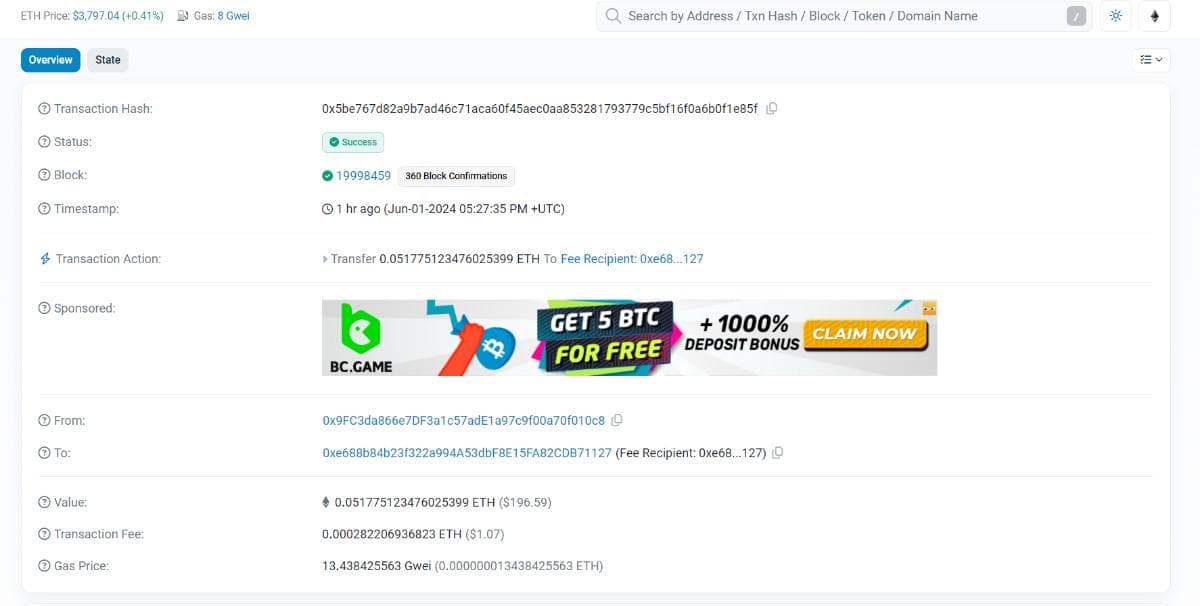
The transaction details page shows the status, block number, timestamp, sender’s address, receiver’s address, value, transaction fee, and gas price.
A Token is a digital representation of an asset on a blockchain such as Ethereum, Polygon, or Polkadot. EVM tokens use the Ethereum Virtual Machine runtime for smart contracts, e.g., ERC-20 tokens like Fantom, Circle USD, and Tether.
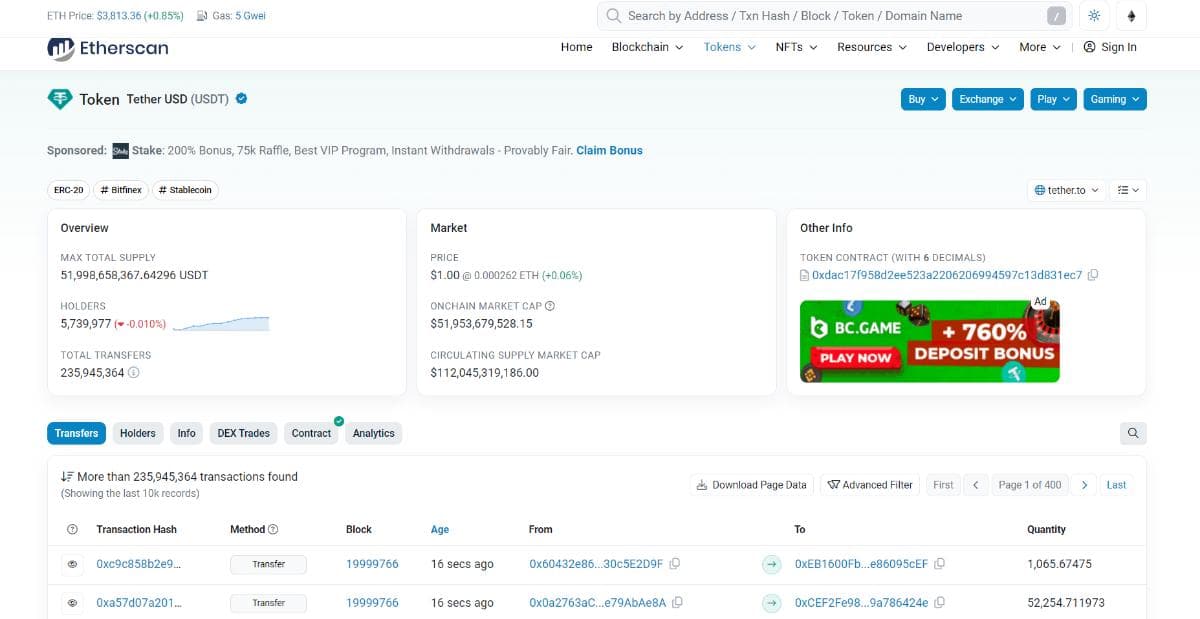
The overview shows total supply, number of holders, transfers, and token analytics. Tokens are governed by smart contracts, ensuring transparency.
In Ethereum, a block is a collection of transactions and data. Each block contains a hash and links to the previous block, forming the blockchain.
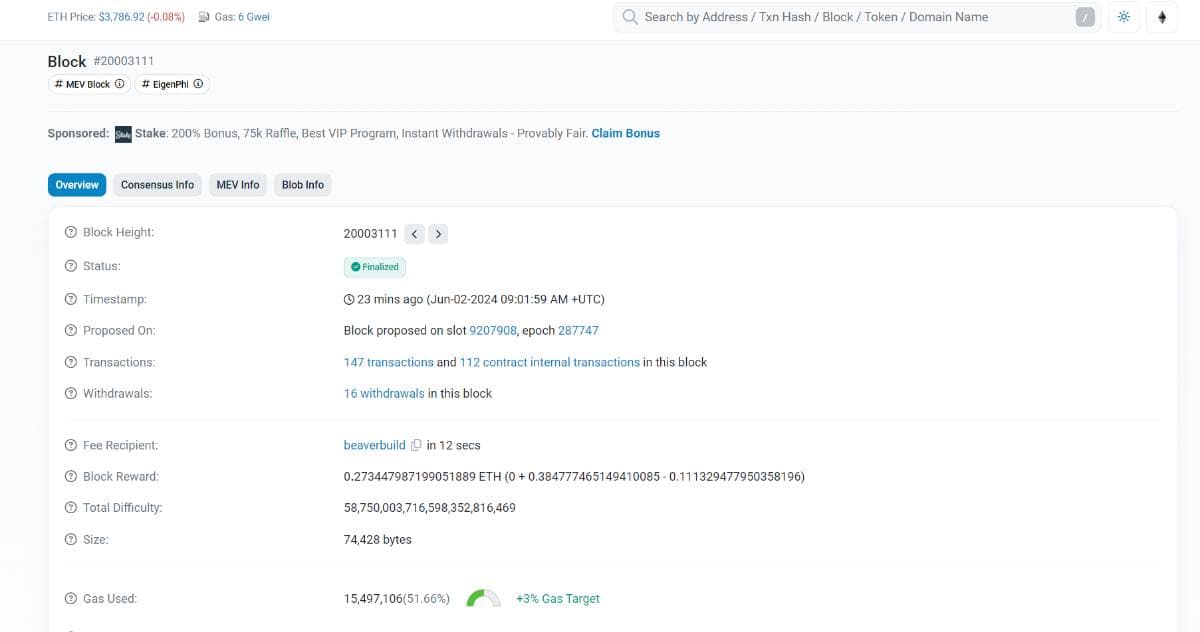
Block details include height, finalization status, timestamp, and validator rewards.
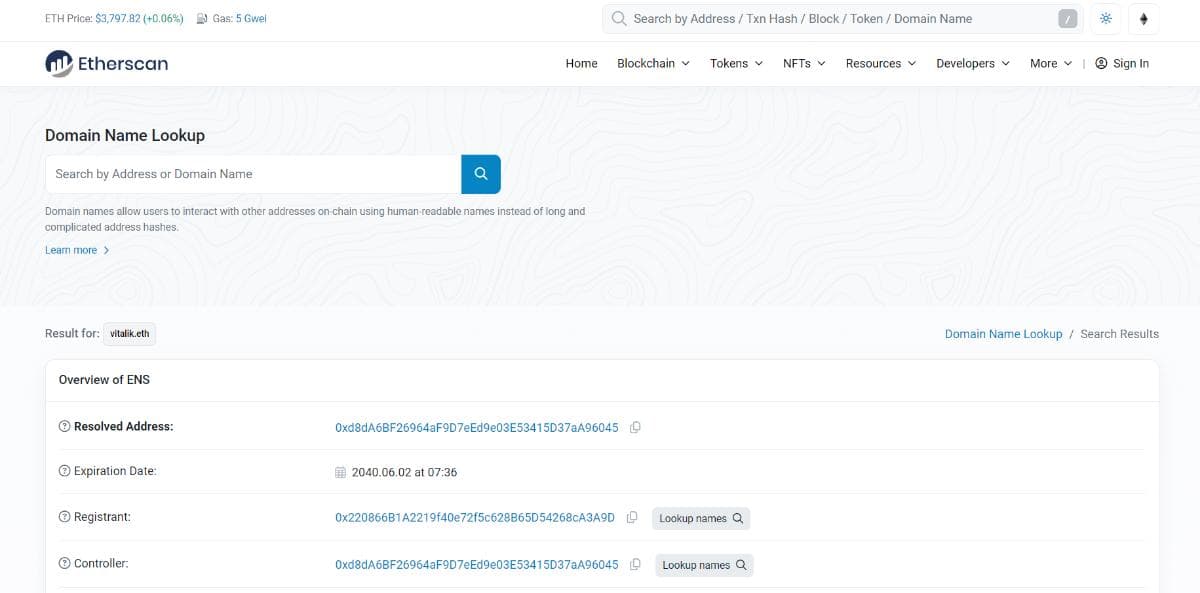
Ethereum Name Service converts Ethereum addresses into recognizable domain names, like vitalik.eth. Searching by domain name shows the resolved address and associated transactions.
Etherscan offers insights into Ethereum activity, tokens, charts, and APIs for developers to build products. Explore features like top Ethereum holders, token trackers, NFT transfers, and more.
India Crypto Research operates independently. The information presented herein is intended solely for educational and informational purposes and should not be construed as financial advice. Before making any financial decisions, it's essential to undertake your own thorough research and analysis. If you're uncertain about any financial matters, we strongly recommend seeking guidance from an impartial financial advisor.